Python – While Loop
Python – While Loop: A loop statement allows a programme to repeat a set of instructions under certain conditions. This allows a programmer to build programmes with fewer lines of code and improve the readability of the code. To meet looping requirements, Python includes the following types of loops:
- while loop
- for loop
The While Loop
The Python – While Loop allows you to repeat a group of statements as long as a certain condition is true. It may be thought of as a looping if statement. When the number of iterations is unknown, a while loop is chosen over a for loop.
Syntax
while condition: statements
Flow Diagram:
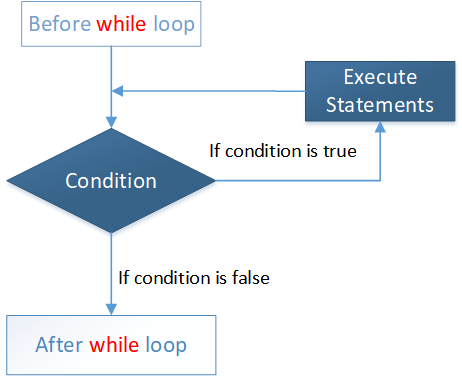
In the example below, the programme utilises a while loop to add all numbers from 1 to 5.
sum = 0 i = 1 while (i < 6): sum = sum + i i = i+1 print(sum)
The output of the above code will be:
15
While loop with else statement
The else block can also be used inside a while loop. When the condition check in the while loop returns false, the else block is invoked.
Syntax
while condition: statements else: statements
After exiting the while loop, the else code block is executed in the example below.
i = 1
while (i < 6):
print(i)
i = i + 1
else:
print('loop exhausted.')
The output of the above code will be:
1 2 3 4 5 loop exhausted.
When the programme exits the while loop using break statements, however, the else block is ignored.
i = 1
while (i < 6):
print(i)
i = i + 1
if (i==4):
break
else:
print('loop exhausted.')
The output of the above code will be:
1 2 3
