Python – Lists
In Python – Lists are a sort of data container that may hold numerous pieces of information in a single variable. It can include components of several data kinds. A list’s elements are sorted and may be retrieved using an index number.
Create List
A Python – Lists may be made by using a comma to separate the components and surrounding them with square brackets []. It may also be made with the help of the list() function and list comprehension.
#List with multiple datatypes
Info = ['John', 25, 'London']
print(Info)
#Creating list using list function
colors = list(('Red', 'Blue', 'Green'))
print(colors)
#Creating list using list comprehension
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y = [i*i for i in x]
print(y)
The output of the above code will be:
['John', 25, 'London'] ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Access element of a List
The index number of a list element can be used to access it. The index number in Python begins with 0 in the forward direction and -1 in the reverse direction. The indexing notion of a list is depicted in the diagram below.
List Indexing:
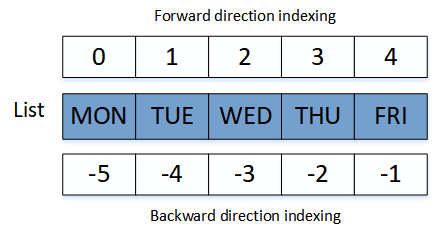
The following example shows how to use the index number to retrieve elements of a Python – Lists.
weekday = ['MON', 'TUE', 'WED', 'THU', 'FRI'] #forward indexing print(weekday[1]) #backward indexing print(weekday[-1])
The output of the above code will be:
TUE FRI
Access range of elements of a List
A statement like [startIndex: endIndex] can be used to pick a range of entries from a list, with end index being omitted. If start index and end index aren’t specified, the first and last index numbers in the list will be used instead.
weekday = ['MON', 'TUE', 'WED', 'THU', 'FRI'] print(weekday[1:3]) print(weekday[-5:-1],"\n") print(weekday[1:]) print(weekday[:-3],"\n") print(weekday[:])
The output of the above code will be:
['TUE', 'WED'] ['MON', 'TUE', 'WED', 'THU'] ['TUE', 'WED', 'THU', 'FRI'] ['MON', 'TUE'] ['MON', 'TUE', 'WED', 'THU', 'FRI']
Modify the value of an Element
To update the value of an element, use its index to assign a new value.
Info = ['John', 25, 'London'] #value at index=0 changed to 'Marry' Info[0] = 'Marry' print(Info)
The above code will give the following output:
['Marry', 25, 'London']
Add elements in a List
To add elements to a list, use the techniques listed below:
- append() – add an element to the end of a list.
- insert() – insert an element at the specified index of the list.
days = ['MON', 'TUE', 'WED', 'THU', 'FRI', 'SAT']
# add this element in last of the list
days.append('SUN')
print(days)
month = ['JAN', 'FEB', 'MAR', 'MAY']
# add 'APR' at index=3 of the list
month.insert(3,'APR')
print(month)
The output of the above code will be:
['MON', 'TUE', 'WED', 'THU', 'FRI', 'SAT', SUN'] ['JAN', 'FEB', 'MAR', 'APR', 'MAY']
Delete elements of a List
To remove elements from a list, use the methods/keywords listed below:
- remove() – deletes the first occurrence of a specified element from the list.
- pop() – deletes element at specified index or last element if index is not specified.
- clear() – deletes all elements of a list.
- del – deletes an element or range of elements or list itself.
number = [10, 50, 50, 100, 1000] #delete first occurrence of 50. number.remove(50) print(number) number = [10, 50, 50, 100, 1000] #delete element at index=3. number.pop(3) print(number) number = [10, 50, 50, 100, 1000] #delete last element from the list. number.pop() print(number) number = [10, 50, 50, 100, 1000] #delete all elements from the list. number.clear() print(number)
The above code will give the following output:
[10, 50, 100, 1000] [10, 50, 50, 1000] [10, 50, 50, 100] []
The del keyword is used to delete an element or range of elements or list itself.
number = [10, 50, 50, 100, 1000] #delete element at index=3. del number[3] print(number) number = [10, 50, 50, 100, 1000] #delete element at index=1,2 and 3. del number[1:4] print(number) number = [10, 50, 50, 100, 1000] #delete list 'number'. del number print(number)
The above code will give the following output:
[10, 50, 50, 1000]
[10, 1000]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "Main.py", line 14, in <module>
print(number)
NameError: name 'number' is not defined
List Length
To determine the total number of entries in a list, tuple, set, or dictionary, use the len() function.
number = [10, 50, 50, 100, 1000, 1000] print(len(number))
The output of the above code will be:
6
Loop over List
For loop over List:
for loop can be used to access each element of a list.
colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green']
for x in colors:
print(x)
The output of the above code will be:
Red Blue Green
While loop over List
Each member of a list may be retrieved using the while loop and the len() method.
colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green']
i = 0
while i < len(colors):
print(colors[i])
i = i + 1
The above code will give the following output:
Red Blue Green
Check an element in the List
If the control statement is used to determine whether or not the list includes the supplied element.
colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green']
if 'white' in colors:
print('Yes, white is an element of colors.')
else:
print('No, white is not an element of colors.')
The above code will give the following output:
No, white is not an element of colors.
Copy List
There are a few options for making a copy of the list.
- = operator: Creates a reference of the list. Any change in old list modifies new list also.
- copy(): Creates an independent copy of a list.
- list(): Creates an independent copy of a list.
colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] mycolor = colors yourcolor = colors.copy() hiscolor = list(colors) print(mycolor) print(yourcolor) print(hiscolor, "\n") #delete last element in 'colors' colors.pop() print(mycolor) print(yourcolor) print(hiscolor)
The output of the above code will be:
['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] ['Red', 'Blue'] ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green']
Join Lists
There are a few different methods to join a list.
- + operator: Used to join two lists into a new list.
- append(): Appends all elements of one list into another.
- extend(): Adds all elements of one list into another.
colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] numbers = [10, 20] mylist1 = colors + numbers print(mylist1) colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] numbers = [10, 20] for i in numbers: colors.append(i) print(colors) colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green'] numbers = [10, 20] colors.extend(numbers) print(colors)
The output of the above code will be:
['Red', 'Blue', 'Green', 10, 20] ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green', 10, 20] ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green', 10, 20]
