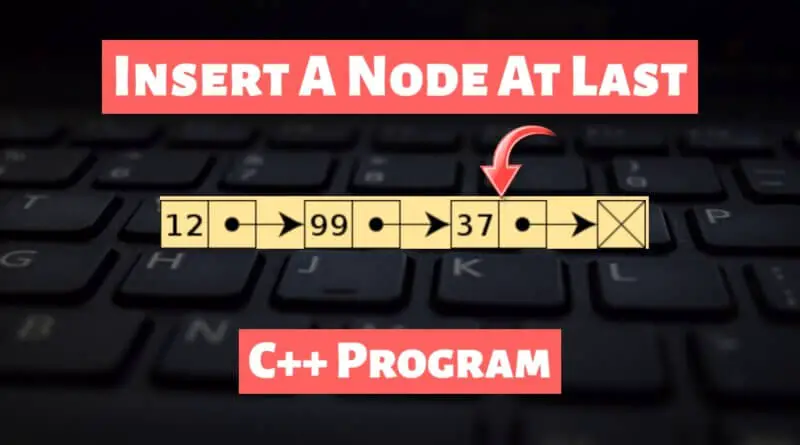
Insert A Node At End In Linked List using C++
Technology and generation are growing up together, and the younger generation users are somewhat connected with tech and the internet all the time. Not to mention, today the whole world in this time of crisis is working over the internet. But to make these technologies, software, etc a software developer must have excellent problem-solving skills. In this world where the internet is the new fuel, one needs to be pretty sharp. And by sharp, for software developers, it means knowing how to automate real-world problems using computer programs. Data structures help a lot in this journey of logic building. So today we’re going to write a simple data structure program to Insert A Node At the End In Linked List using C++.
What is A Linked List?
A linked list is a basic list of nodes containing different elements for all algorithms in data structures. Also, it’s pretty easy to understand.
What’s The Approach?
- Firstly we’ll allocate a new node, by simply creating it.
- Next up we’ll insert the data in this new node.
- Now, the
nextsection of the node is set to null showing the end of the linked list.
- Also,o the
nextsection of our linked list is going to point towards the head of this newly created node.
Also Read: Print Cube Root Of A Number in Java
C++ Program To Insert A Node At End In Linked List
Input:
append(6)
push(7)
Output:
Created Linked List is: 7 6
// C++ program to demonstrate
// insertion methods on Linked List at the end
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A linked list node
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer)
to the head of a list and an int, inserts
a new node on the front of the list. */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* 1. allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* 2. put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* 3. Make next of new node as head */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* 4. move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head
of a list and an int, appends a new node at the end */
void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* 1. allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
Node *last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/
/* 2. put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* 3. This new node is going to be
the last node, so make next of
it as NULL*/
new_node->next = NULL;
/* 4. If the Linked List is empty,
then make the new node as head */
if (*head_ref == NULL)
{
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
/* 5. Else traverse till the last node */
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
/* 6. Change the next of last node */
last->next = new_node;
return;
}
// This function prints contents of
// linked list starting from head
void printList(Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout<<" "<<node->data;
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* head = NULL;
// Insert 6. So linked list becomes 6->NULL
append(&head, 6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes 7->6->NULL
push(&head, 7);
cout<<"Created Linked list is: ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}